Reproducibility
The Benefits of Reproducible Data¶
Data changes frequently. This makes the task of keeping track of its exact state over time difficult. Oftentimes, people maintain only one state of their data - its current state.
This has a negative impact on the work, as it becomes hard to:
- Debug a data issue
- Validate machine learning training accuracy (re-running a model over different data gives different results)
- Comply with data audits, and model audits in particular
In comparison, lakeFS exposes a Git-like interface to data that allows keeping track of more than just the current state of data. This makes reproducing its state at any point in time straightforward.
Achieving Reproducibility with lakeFS¶
To make data reproducible, we recommend taking a new commit of your lakeFS repository every time the data in it changes. As long as there’s a commit taken, the process to reproduce a given state is as simple as reading the data from a path that includes the unique commit_id generated for each commit.
To read data at it’s current state, we can use a static path containing the repository and branch names. To give an example, if you have a repository named example with a branch named main, reading the latest state of this data into a Spark Dataframe is always:
Example
The code above assumes that all objects in the repository under this path are stored in parquet format. If a different format is used, the applicable Spark read method should be used.
Using Commits¶
In a lakeFS repository, we are capable of taking many commits over the data, making many points in time reproducible.
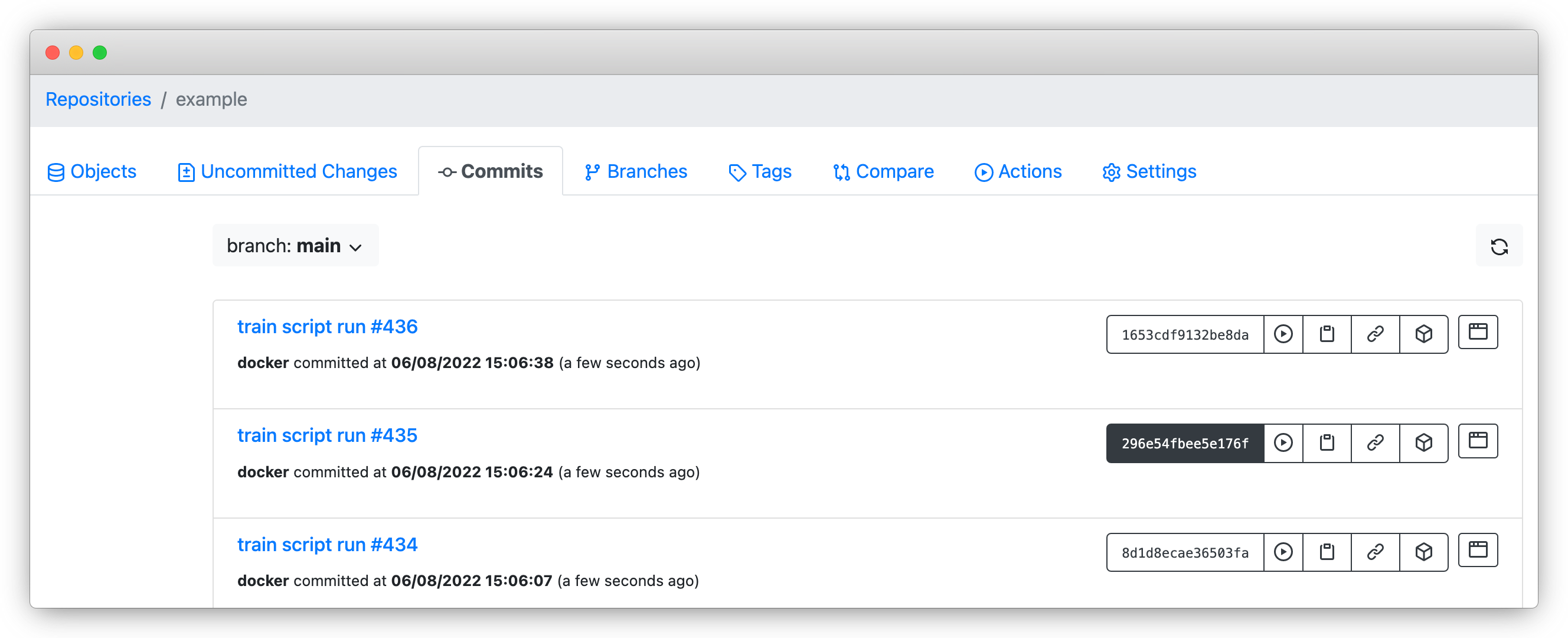
In the repository above, a new commit is taken each time a model training script is run, and the commit message includes the specific run number.
If we wanted to re-run the model training script and reproduce the exact same results for a historical run, say run #435, we could copy the commit ID associated with the run and read the data into a dataframe like so:
df = spark.read.parquet("s3://example/296e54fbee5e176f3f4f4aeb7e087f9d57515750e8c3d033b8b841778613cb23/training_dataset/")
The ability to reference a specific commit_id in code simplifies reproducing the specific state a data collection or even multiple collections. This has many applications that are common in data development, such as historical debugging, identifying deltas in a data collection, audit compliance, and more.
Using Tags¶
In addition to commits, lakeFS supports tags. A tag is a human-readable label that points to a specific commit.
Tags are useful when you want to mark important points in time, such as: * A production data release * A specific model training dataset * A dataset used for an audit
Instead of referencing a non-readable commit_id, you can reference the tag directly in your code. For example:
Here, v1.0 is a tag that points to a specific commit. A tag is an immutable reference, it cannot be modified after creation
(only deleted and recreated). Therefore, reading data through a tag will always return the exact same data state.
Using tags makes it easier to work with reproducible datasets in a way that is readable, shareable, and stable over time.